< Page 6 of 15 >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Anti-Reflection
Coating
Technical Aspects
 Only
92 percent of light entering an uncoated CR-39 lens is transmitted through
the lens; with a multi-layer coating that number increases to nearly
99.5 percent. Both sides of a lens should be coated to maximize efficiency.
A multi-layered anti-reflection coating for the lenses will improve
the aesthetics of a high refractive index material (1.6 or greater)
more than CR 39 because high refractive index materials naturally reflect
more light. A material with a refractive index of 1.6 transmits only
about 87 percent of incident light with 13 percent lost to reflections.
An anti-reflection coating will increase the percentage of transmitted
light from 87 percent to 99 percent. AR coating is also especially effective
with aspheric lenses since the flatter back surfaces tend to create
more back side reflections.
Only
92 percent of light entering an uncoated CR-39 lens is transmitted through
the lens; with a multi-layer coating that number increases to nearly
99.5 percent. Both sides of a lens should be coated to maximize efficiency.
A multi-layered anti-reflection coating for the lenses will improve
the aesthetics of a high refractive index material (1.6 or greater)
more than CR 39 because high refractive index materials naturally reflect
more light. A material with a refractive index of 1.6 transmits only
about 87 percent of incident light with 13 percent lost to reflections.
An anti-reflection coating will increase the percentage of transmitted
light from 87 percent to 99 percent. AR coating is also especially effective
with aspheric lenses since the flatter back surfaces tend to create
more back side reflections.
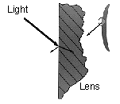
When light enters the lens, a portion of that light is reflected from the front surface; about 4 percent. That means that transmittance is reduced by 4 percent at that point. This happens again on the rear surface of the lens, but for this discussion only the front surface will be considered.
To better understand how AR coating works, lets review the basics of wave theory. We�ll start with an analogy. Imagine two stones thrown into a pond or rain drops hitting a puddle. The waves emerging from two stones or drops of water eventually run into each other canceling each other out. This is actually the theory of �wave interference� at work. There is positive or �constructive interference� and negative or �destructive� interference.
Let�s look at constructive interference with this simple example. One pile of sand added to another equals a pile twice as high. Add a pile of sand to a hole in the ground of the same volume and zero is the result. This is a visual example of destructive interference.
 |
 |
| Constructive
Interfernce Add two piles of sand together and the result is a pile of sand twice as high |
|
 |
 |
| Destructive
Interference Add a pile of sand to a hole in the ground of the same volume and the result is zero. |
|
< Page 6 of 15 >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15