< Page 3 of 13 >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Color
Vision
Light
& Color
| Color | Wavelength |
| Violet | 380 nm |
| Blue | 460 nm |
| Green | 510 nm |
| Yellow | 560 nm |
| Orange | 610 nm |
| Red | 650 nm |
Basic Terminology
Hue refers to the name of the color. When
asked to identify the color of an object, you�ll most likely refer first
to its hue: red, orange, green, blue, etc.
Saturation or Chroma refers to the strength of the color
or how far it is from neutral gray.
Brightness, Lightness, or Luminosity classifies a
color as light or dark. This characteristic describes a color�s luminous
intensity�its degree of �brightness.
How light behaves to produce color
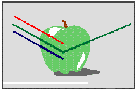
When light comes in contact with an object, it can be reflected, absorbed or transmitted. When light is reflected from an opaque object such as a green apple, for example, the apple is perceived as being green because the red and blue wavelengths are absorbed and the green wavelengths are reflected back to our eyes.
A glass of red grape juice, however, is transparent. So if a light is shown through the juice and a piece of paper is held up on the other side, red light is transmitted to the paper. This is similar to putting a red filter over the lens of a projector. The color red will be transmitted to the screen. Our eyes see the color as red because the juice or the red filter absorbs the green and blue components of white light and transmits the red wavelength.
For an object to appear as black all the wavelengths of light are being absorbed and no light is being reflected from it to our eyes.

< Page 3 of 13 >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13